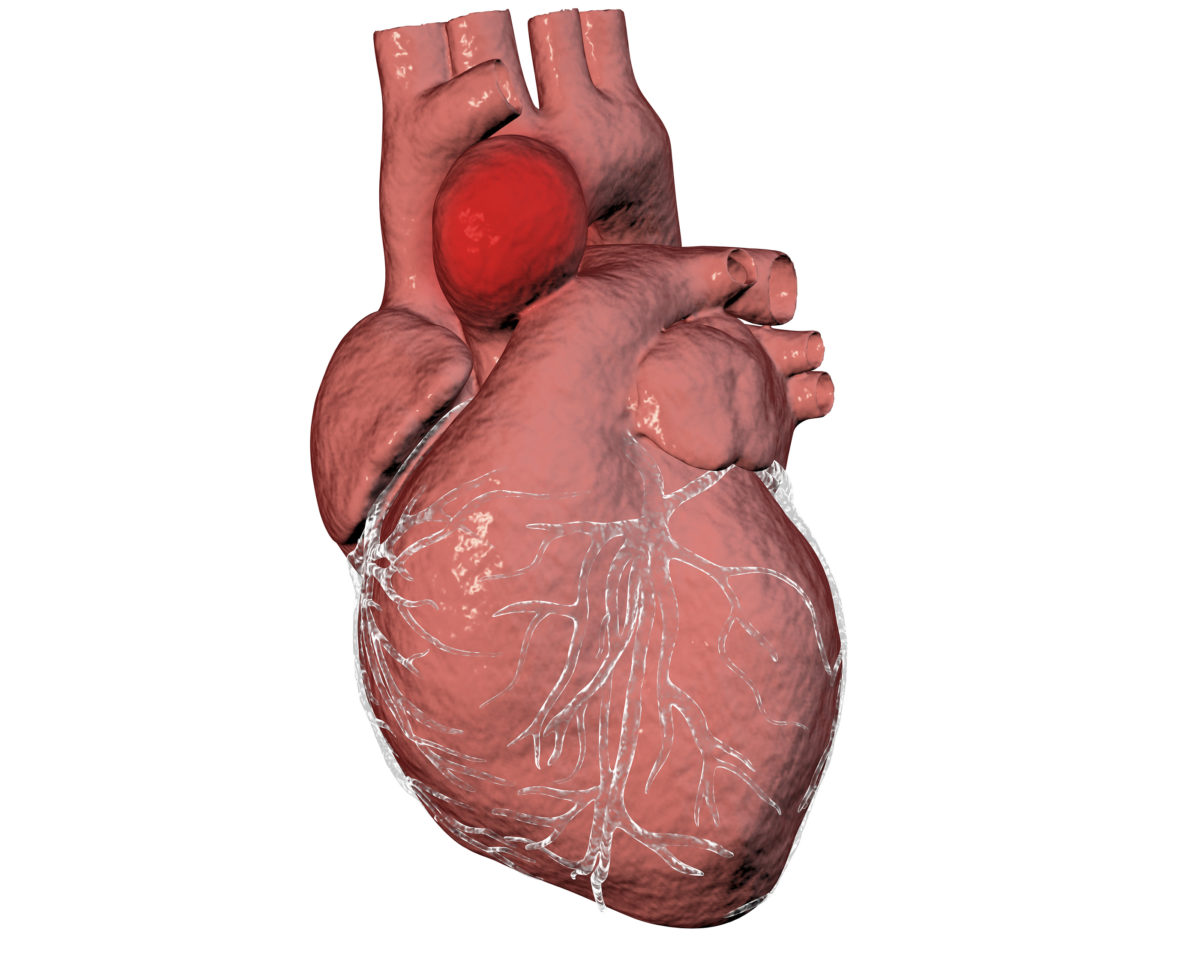
If a person has heart valve disease, it’s not uncommon to also experience other conditions or disorders at the same time, including atrial fibrillation and coronary artery disease. Another disease that can affect patients with heart valve disease is an aortic aneurysm. What is an aortic aneurysm? An aortic aneurysm is when the walls of the aorta (the largest blood vessel in the body) begin to weaken and bulge. This aneurysm can result in a blood leak into the body if it bursts; however not all aortic aneurysms burst. Aortic aneurysms also can force blood away from organs and tissues resulting in heart attacks, kidney damage, stroke, and death.
Bicuspid aortic valve disease is often linked to ascending aortic and aortic root aneurysms. Patients with bicuspid aortic valve disease should also be evaluated for aortic aneurysms.
An aortic aneurysm can appear in the chest (thoracic aortic aneurysm) or in the abdomen (abdominal aortic aneurysm). Chest aneurysms often develop due to genetics, but other causes include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, plaque buildup, or a traumatic injury. With this type of aneurysm, the symptoms are often not present until the aneurysm is large or bursts. Symptoms that a person may experience can include chest pain, back pain, difficulty breathing and/or swallowing, and shortness of breath.
Often, there are no signs of an abdominal aortic aneurysm; however, some people may have back pain, deep pain on the side of the abdomen, or a throbbing sensation near the navel. If this aneurysm bursts, a person can feel sick and vomit, become sweaty, become dizzy, or feel extreme pain in the abdomen or the stomach. Doctors are not certain what causes abdominal aortic aneurysms but some things that may contribute to its development include hardening of the arteries, smoking, high blood pressure, and genetics.
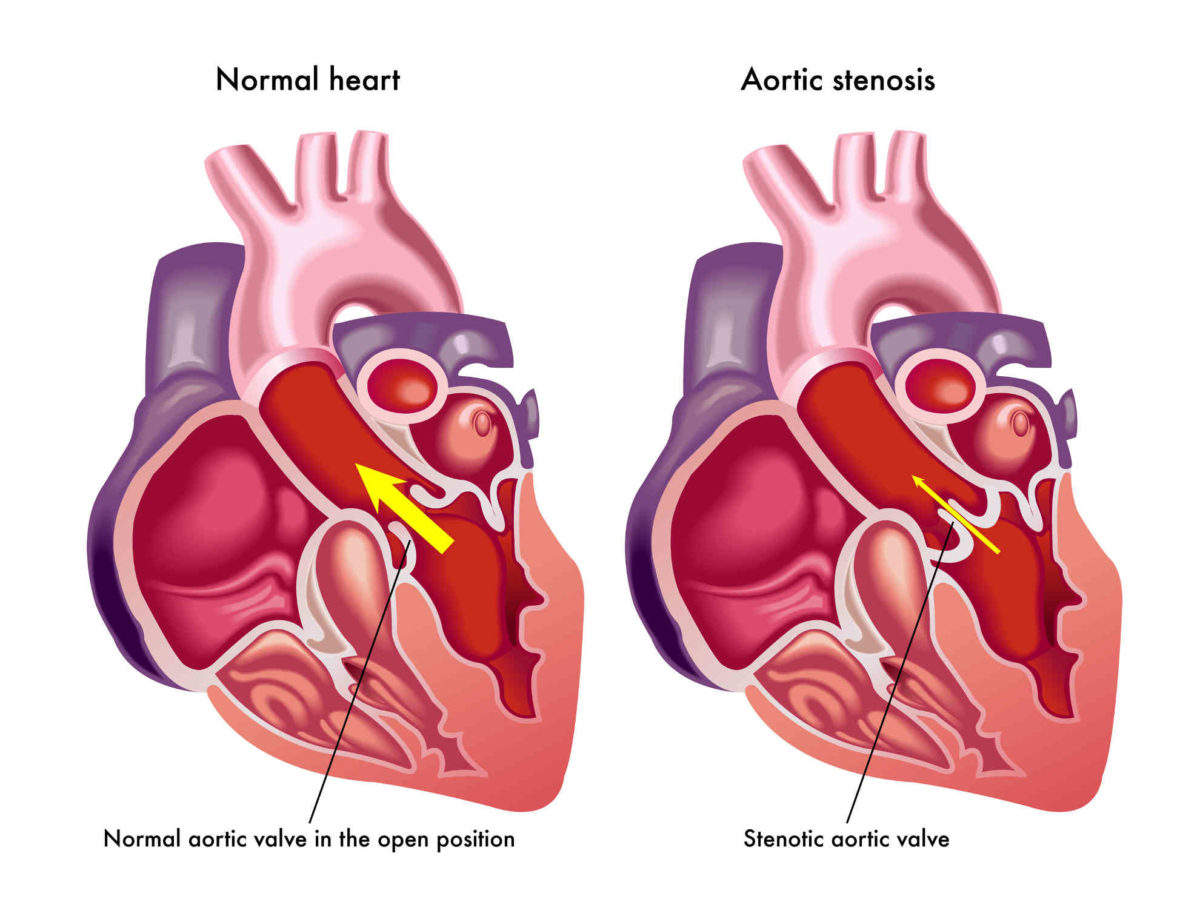
In some cases, aneurysms can actually cause aortic valve disease or dysfunction. How? The aortic root is connected to the aortic valve and the stretching of the root can stretch the valve, which can lead to valve leakage or insufficiency. Patients with aortic aneurysms usually get checked for aortic valve problems, too.
Aneurysms often take years to grow, and they should be taken seriously. To prevent the development of an aneurysm, it’s best to maintain a good blood pressure and to avoid activities and exercise that require intense straining.
If you have an aortic aneurysm and aortic valve disease, talk to a valve specialist to determine a specialized treatment plan for your condition. Dr. Peter Mikhail is a cardiac surgeon who specializes in aortic valve surgery. To book a consult, click here or call 727-312-4844.