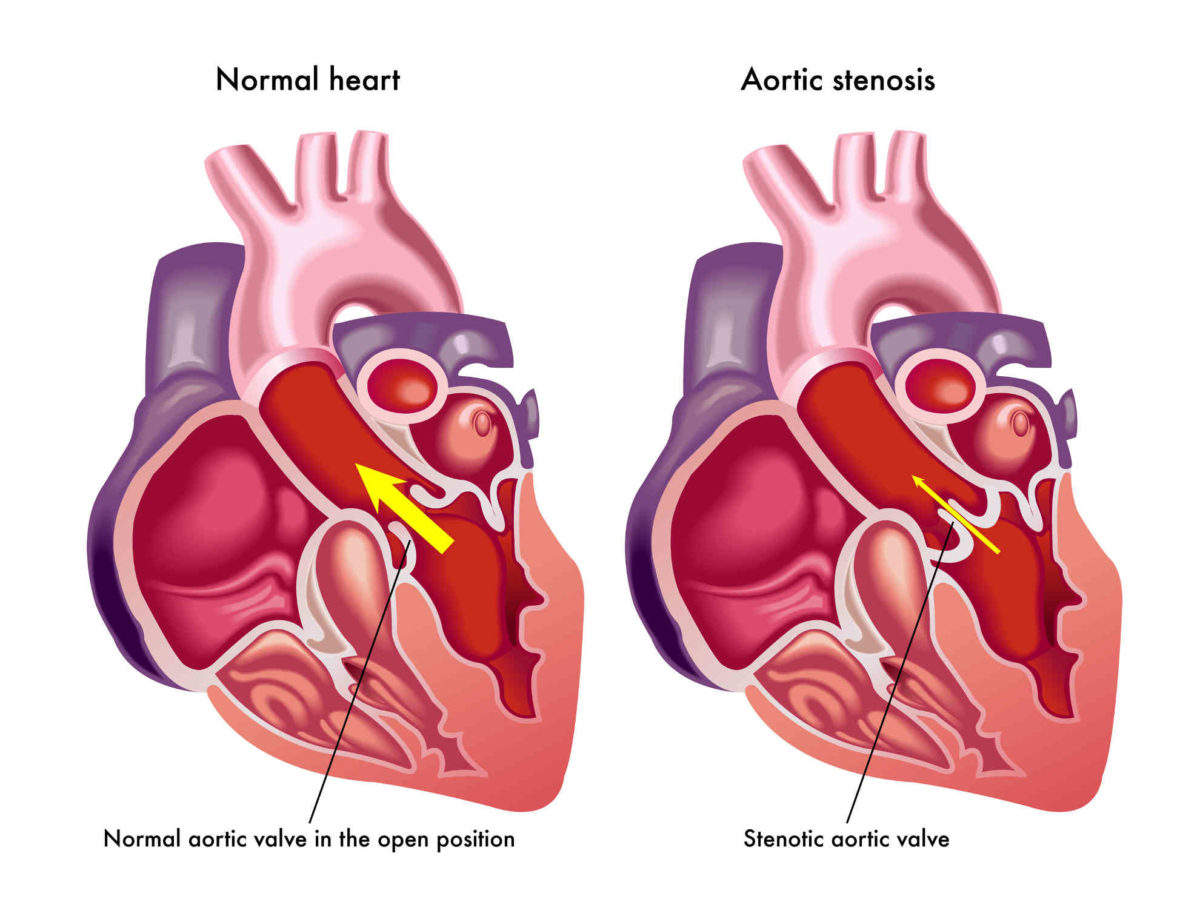
Aortic stenosis is a condition that is growing as the U.S. population grows. Right now, it is estimated that 2.5 million Americans over 75 suffer from this heart valve disease, which accounts for 12.4 percent of the population. Between now and 2050, the elderly population will more than double to around 80 million.
Aortic stenosis affects men more often than women. In fact, 80 percent of adults with aortic stenosis are male. What is aortic stenosis exactly? With this condition, the aortic valve’s flaps (cusps) have thickened or become stiff and could possibly fuse together, which narrows the valve. The valve’s opening becomes narrowed and blocks/reduces blood flow from the heart into the aorta and to the rest of the body.
A person with aortic stenosis will experience the following symptoms: shortness of breath, heart murmur, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, chest tightness, irregular heartbeat, and swelling of the ankles and feet.
The disease is often misdiagnosed and undertreated. A severe case of aortic stenosis can be fatal; some doctors refer to the disease as a “silent killer.” It is a progressive disorder, and the onset of the symptoms and progression will vary from patient to patient. As a person gets older, the aortic valve disease will continue to progress, regardless of what the patient does or doesn’t do.
Since nothing can reduce the progression of this disease, patients are instructed to visit their cardiologist annually, and have an echocardiogram to evaluate is the disease is becoming more severe. Aortic stenosis has three progression stages: mild, moderate, and severe. As stated earlier, a person can experience an array of different symptoms with this disease. If a person is experiencing symptoms, it is often a sign of a progression of the degenerative process, and the person should have the doctor assess them immediately.
If a person gets to the point in which he or she needs an aortic valve replacement, they have more options for surgery than ever before. These days, there are less invasive approaches to aortic valve replacement such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). TAVR is good for people who have been diagnosed with severe aortic valve disease and are at an intermediate or high risk for open heart surgery. Most people who have this procedure are in their 70s or 80s. In this surgery the doctor inserts a catheter in a leg or chest and guides it to the heart. A replacement valve is inserted through the catheter up to the heart.
Do you suffer from aortic stenosis? If you need an aortic valve repair or an aortic valve replacement, Dr. Mikhail is a cardiac surgeon based in New Port Richey, Florida, who specializes in heart valve surgery. To book a consult, click here or call 727-312-4844.